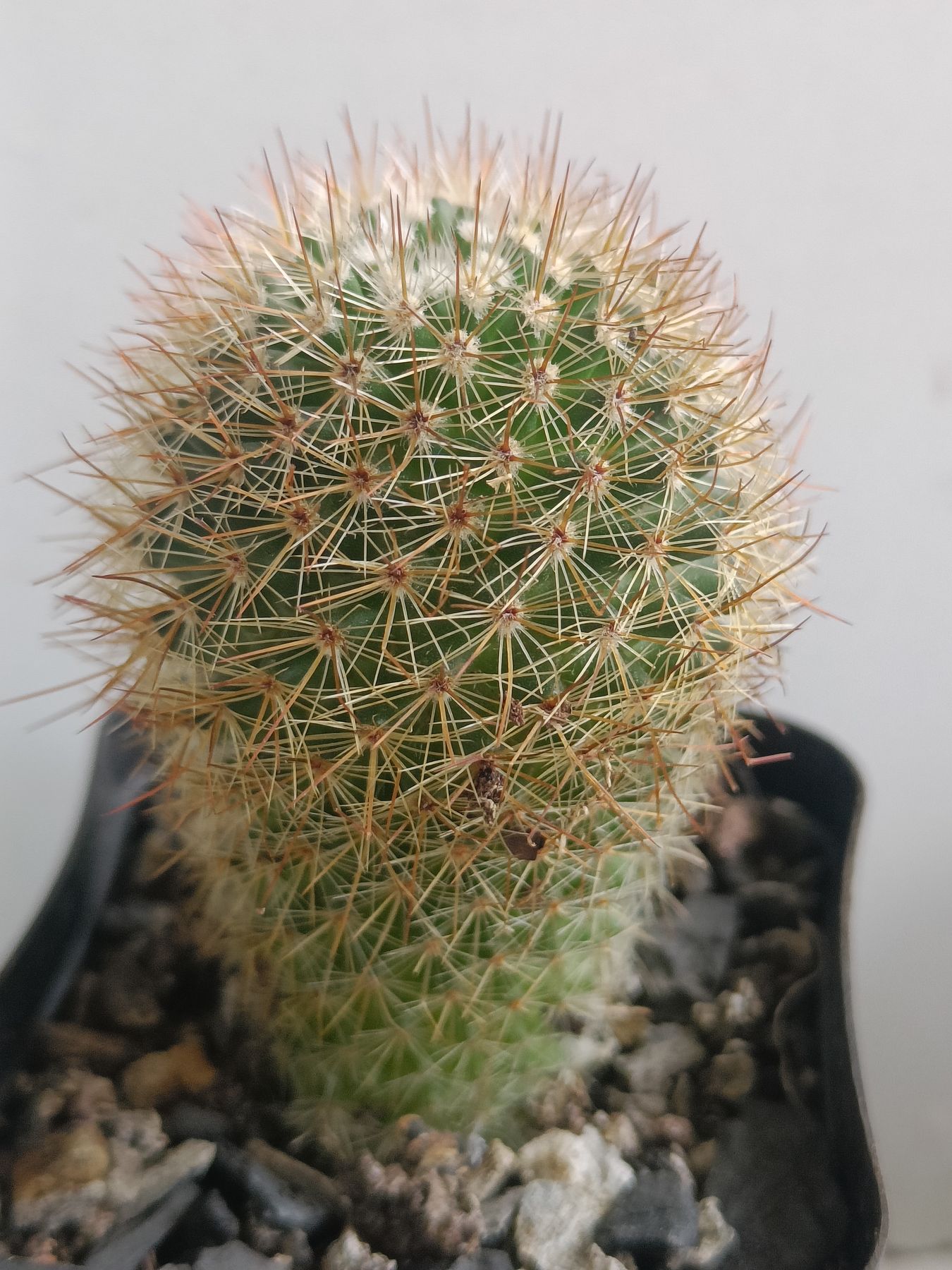
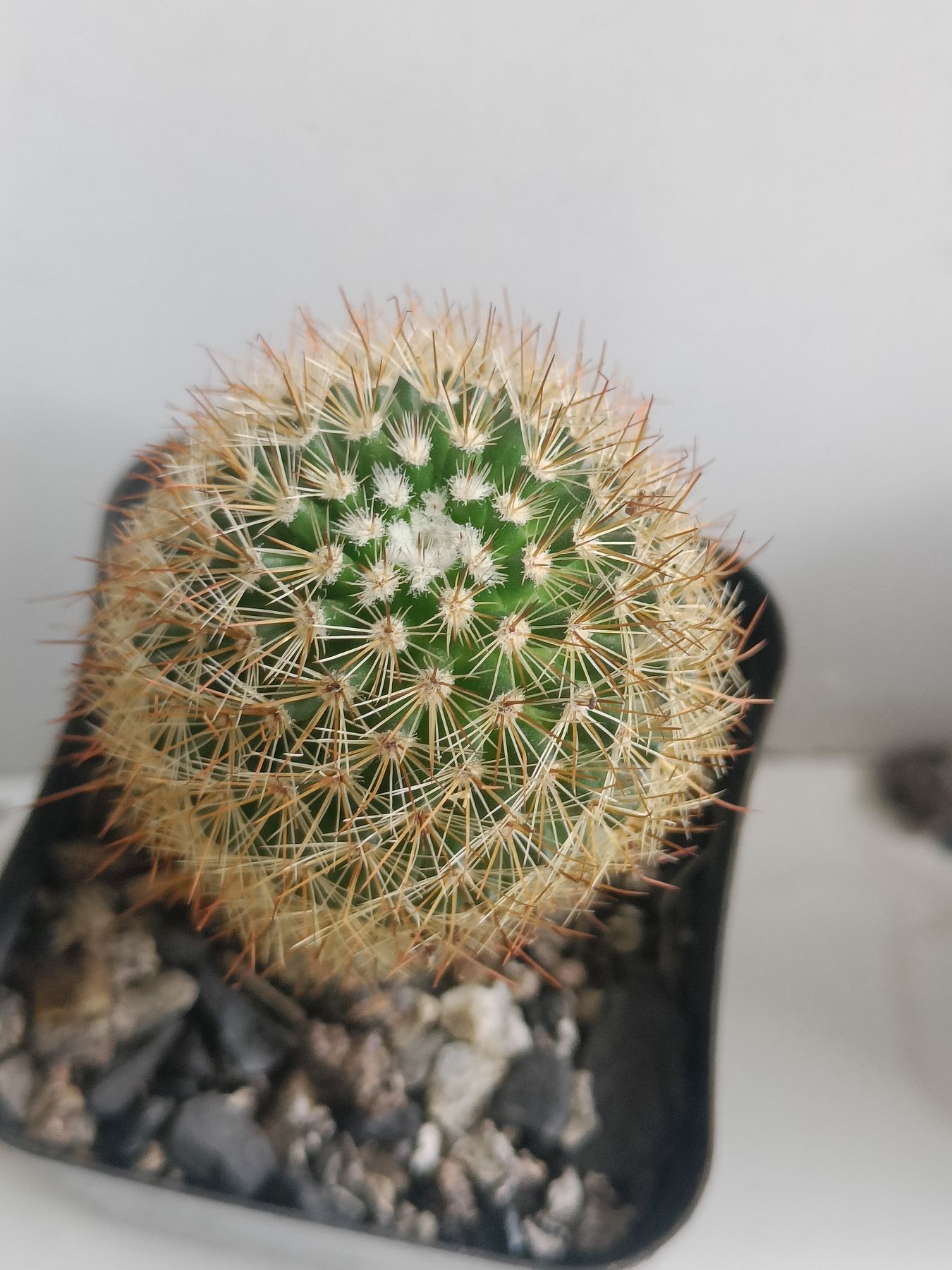
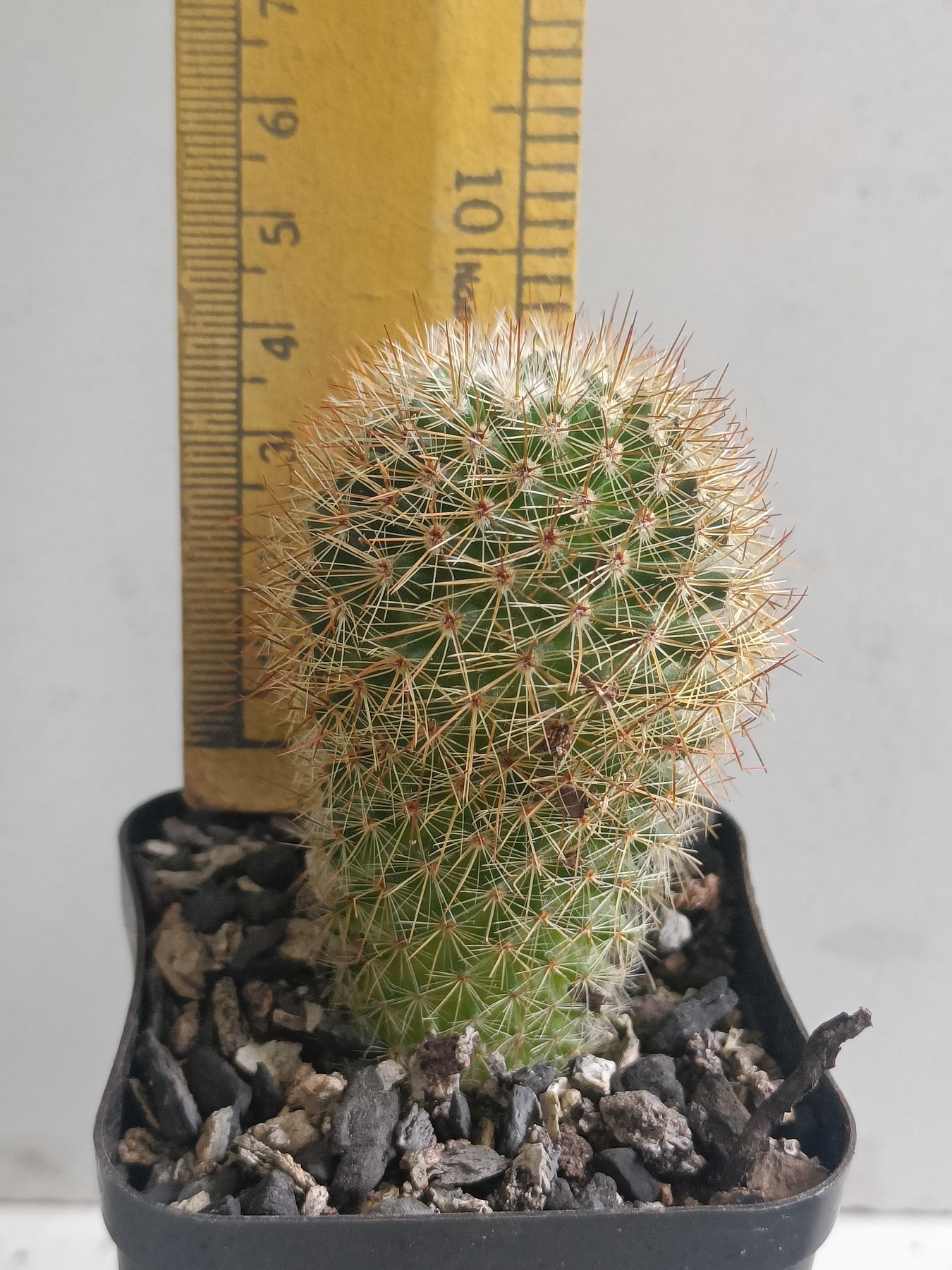
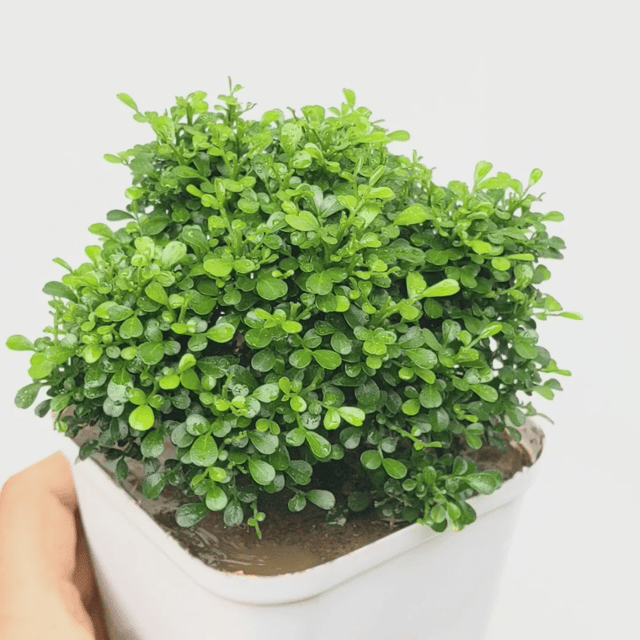
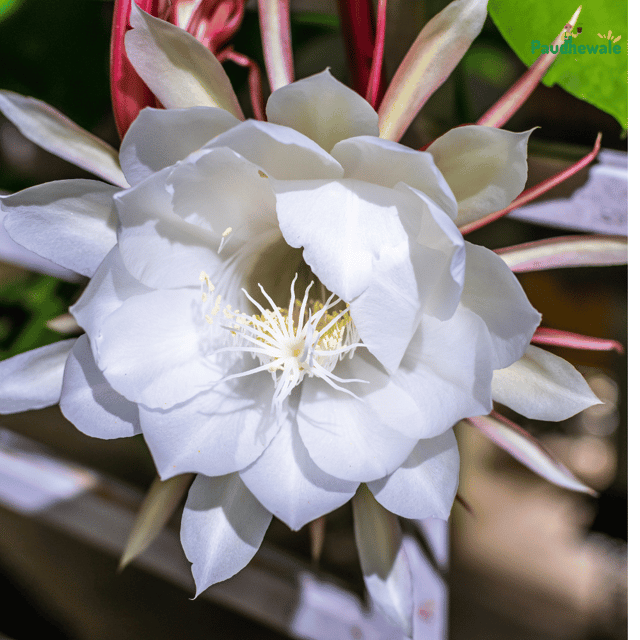
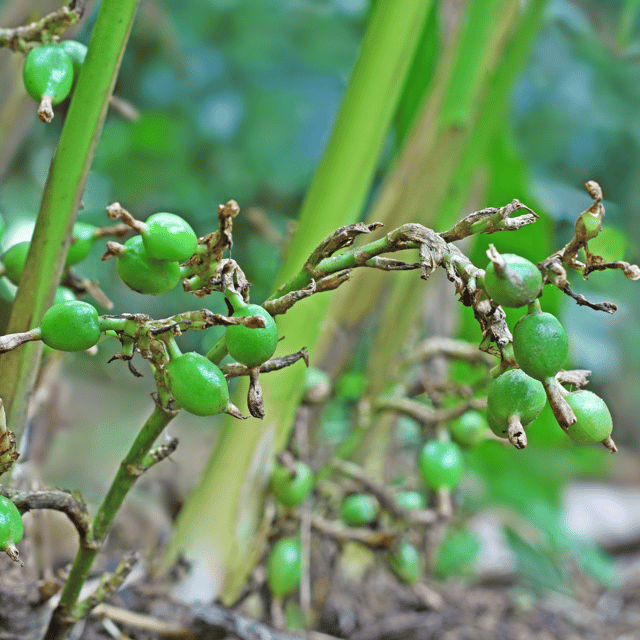
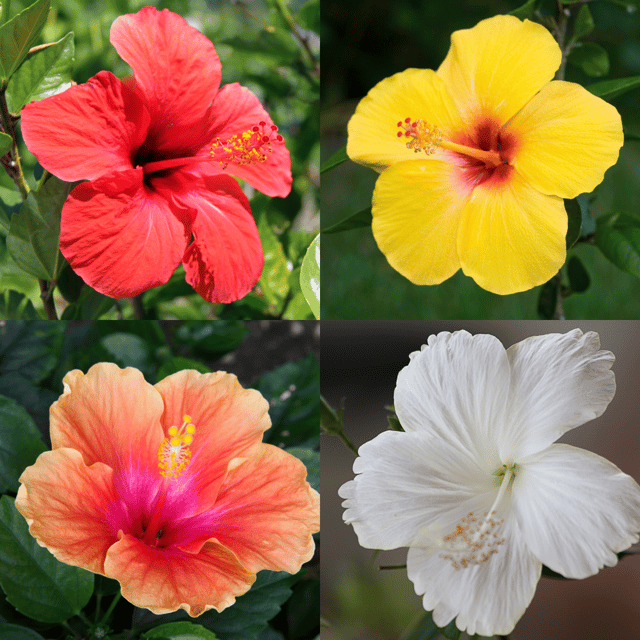
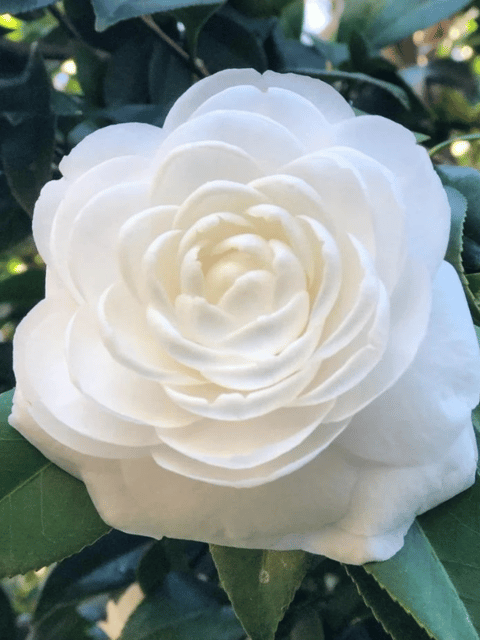
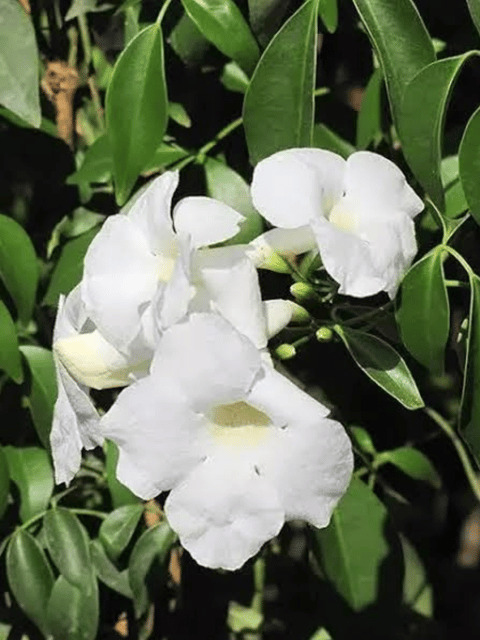
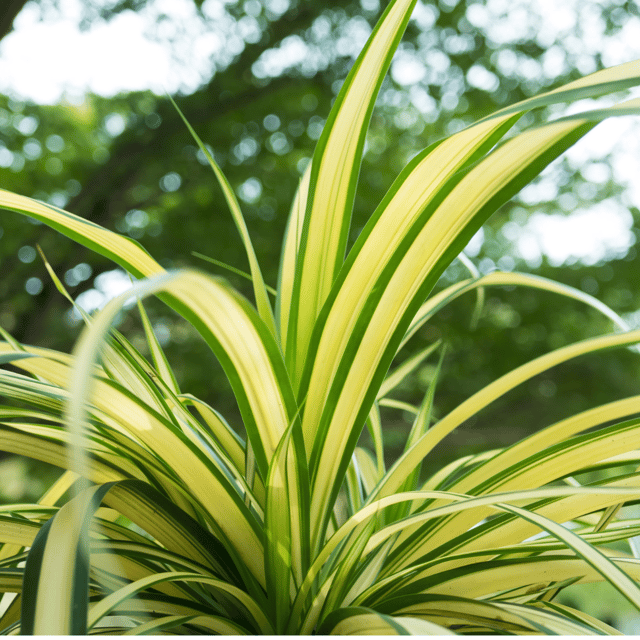
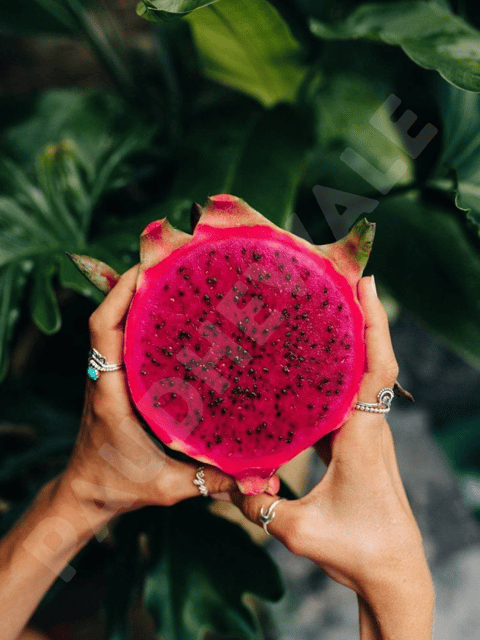
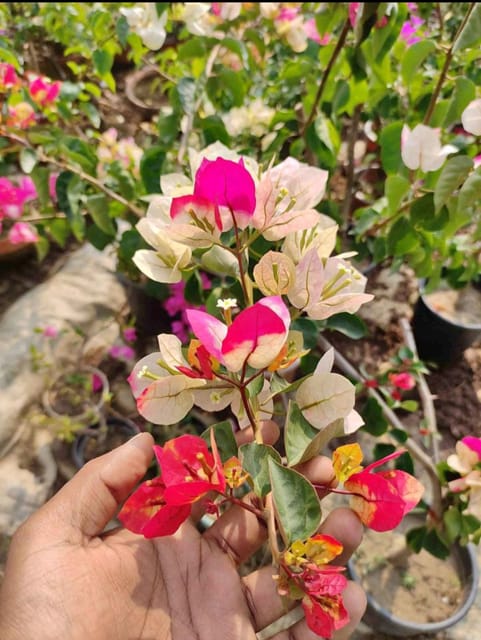
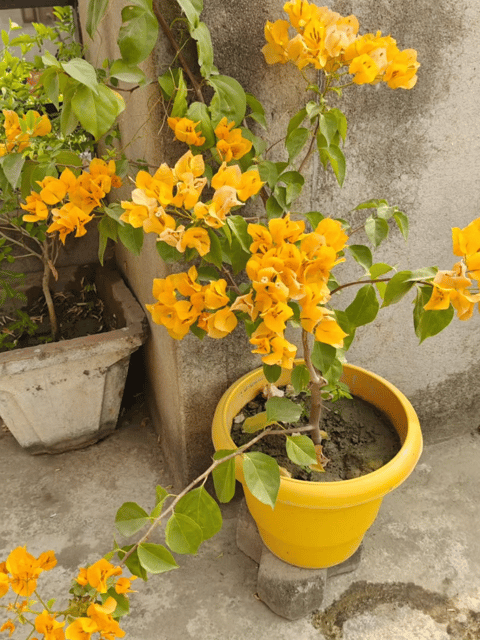
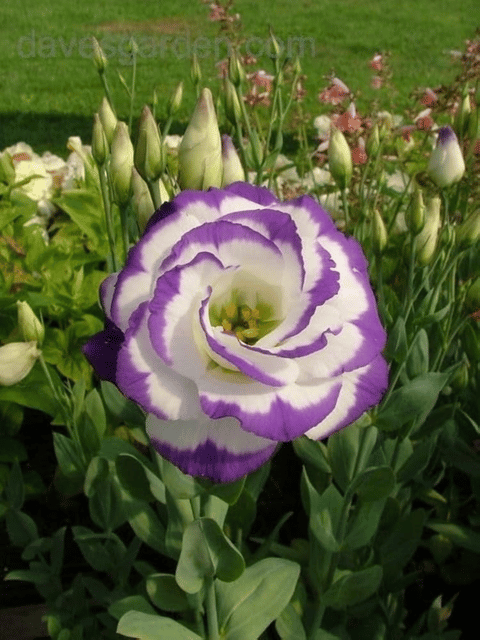
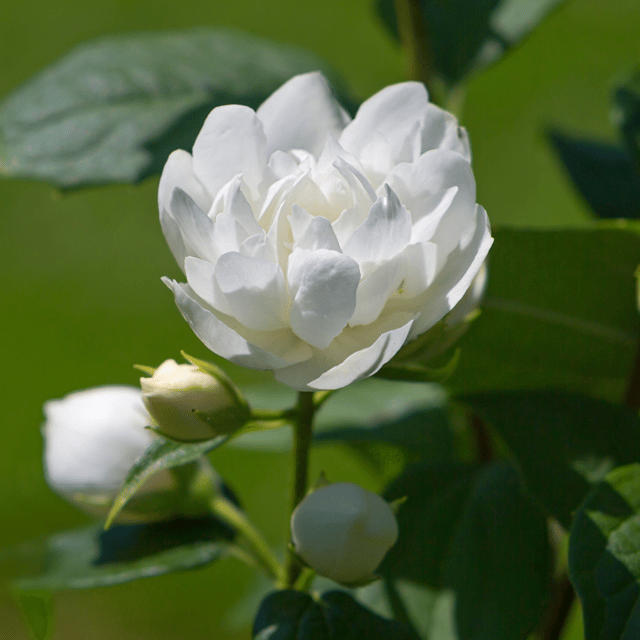
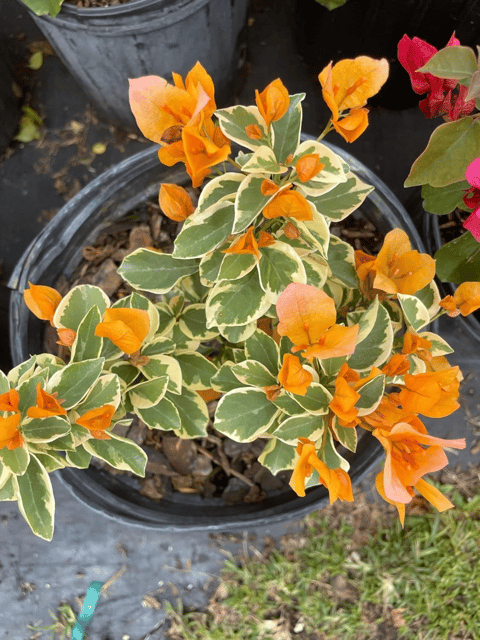
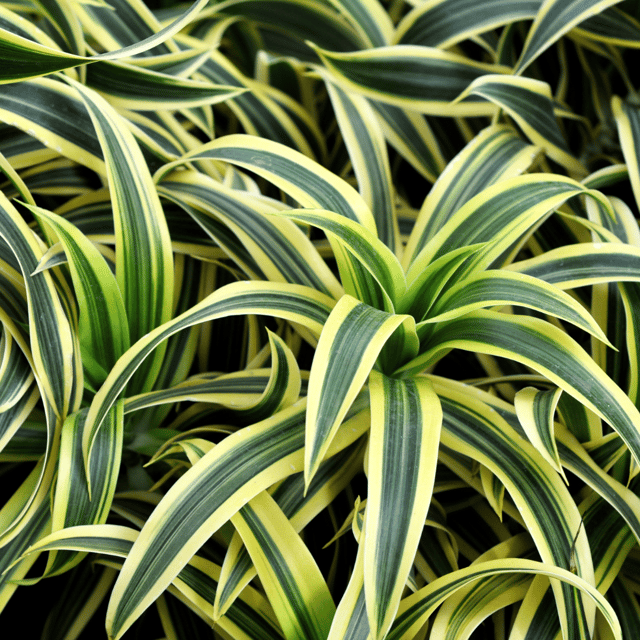
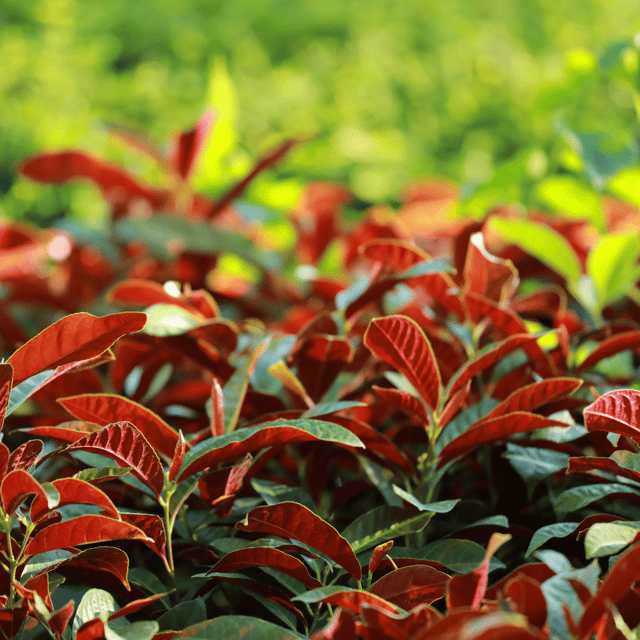
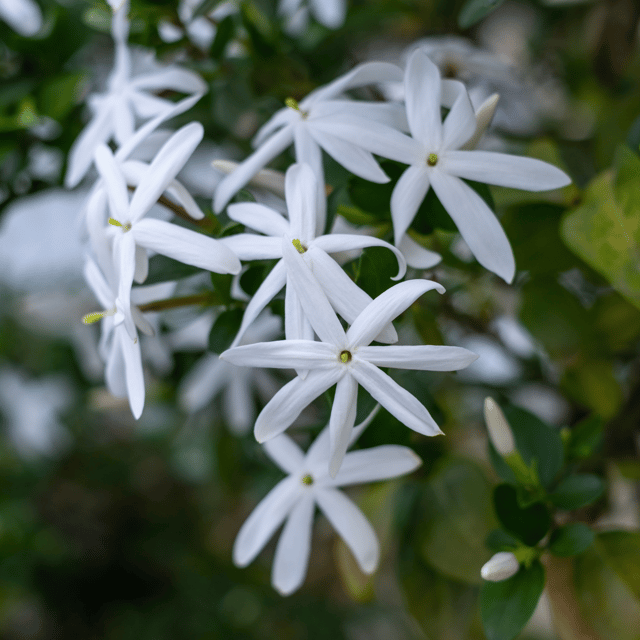
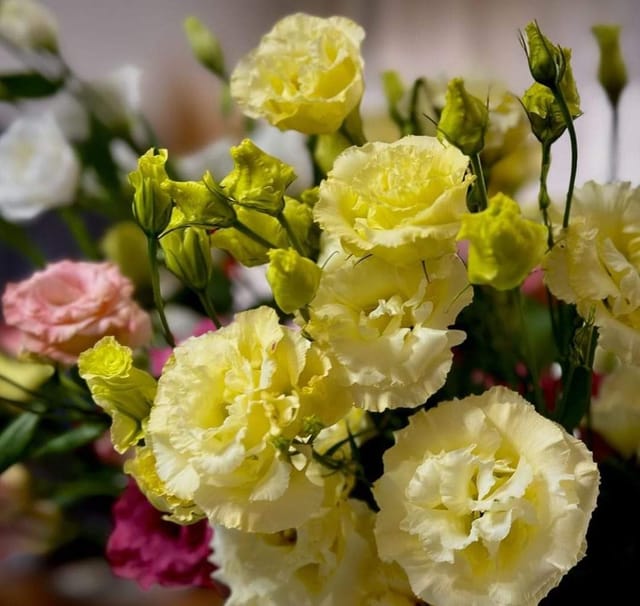
₹499₹249
₹499₹249
₹499₹249
₹1,999₹799
₹599₹299
₹499₹249
₹499₹269
₹599₹269
Pita Putra Nursery
Sold By : Pita Putra Nursery
₹499₹299
₹599₹299
Pita Putra Nursery
Sold By : Pita Putra Nursery
₹499₹299
₹499₹239
₹599₹299
₹499₹249
₹499₹249
₹499₹249
Pita Putra Nursery
Sold By : Pita Putra Nursery
₹599₹299
Pita Putra Nursery
Sold By : Pita Putra Nursery
₹599₹299
₹499₹249